Climate changeMankind is facing a massive task: Reversing the rise in greenhouse gas emissions which has already taken place since industrialisation. Man-made emissions are changing the climate in the long term, thereby endangering the environment and the livelihoods of future generations. Global warming of 1.5° Celsius relative to pre-industrial levels will have a drastic impact on weather events, which will become ever more extreme in the form of long periods of drought and heavy precipitation. This will exacerbate natural hazards and instabilities in the food supply.
|
Switzerland is not immune from the impact of climate change, and global warming is already clearly measurable here!
|
Most emissions occur in the areas of
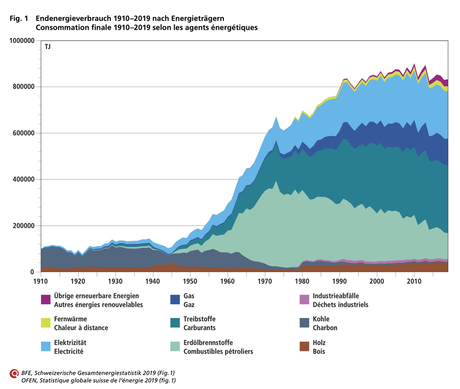
Unfortunately, oil and nuclear energy still play a major role in Switzerland's energy mix. A good half of electricity generation is based on hydropower, while the share of solar energy is only around 4%. |
You can find our sources and more information on this at:
Solar energySolar energy plays a central role in achieving the energy transition. Solar cells convert solar radiation into electrical energy without emitting harmful emissions or generating waste and noise. Another advantage is that photovoltaic (PV) systems can be connected to the public grid or operated autonomously.
In addition, the sharp decline in costs over the past 20 years has made such PV systems economically attractive. Compared to coal and nuclear power, solar energy is already cheaper today if the avoided environmental damage is accounted for. In addition, solar energy scores with its steadily increasing capacity. A PV system is in operation for an average of 30 years, and after one to two years it has recovered the energy that was used to manufacture the system. |
Comparison of different energy sources based on their reliability
|
You can find our sources and more information on this at:
|
Do you want to help push the transition towards solar energy?
|